Configure Calculation Tag
Calculation tag is a kind of special tags, the value of which indicates the calculation result of an formula. The parameter of this formula can be a tag or a constant. Also, the expression can utilize some common calculation methods, including arithmetic & logic operation and trigonometric function, etc..
Calculation tag can perform some relatively complex operations, such as converting the acquired sensor value to the real physical quantity (liquid level, wind speed, etc.), so as to make the computation less intensive for the upper computer as well as the device more intelligent.
Each calculation tag corresponds to one expression which may support at most 8 tags as its input variables. For users' convenience, 8 tags are represented by A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H (case insensitive) in the expression.
Add Calculation Tag
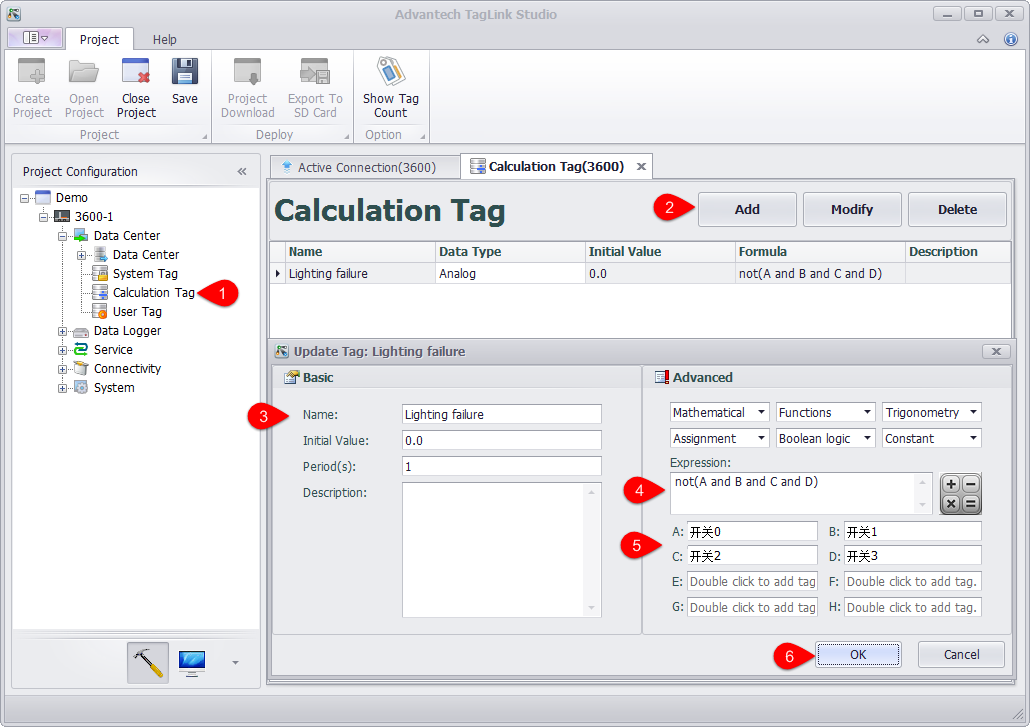
Please follow the procedures to add a calculation tag:
-
Double-click on "Calculation Tag" in the left tree menu.
-
Click "Add" button to add a new calculation tag.
-
Fill in the basic information. "Periods (s)" specifies how often the tags are calculated, and its unit is second.
-
Enter an expression. Uses can select default function or operator from the pull-down lists or type them manually. The example figure shows the calculation expression of "Lighting Failure", the expression logic of which is that the lighting is failed when the value of any tag in four switches is 0.
-
Double-click the variable box to add a tag.
-
Click "OK" button to save the changes.
Expression Check
On the right of "Expression" box there is a calculator button. Click it to open "Calc Expression" window shown as below. This interface is roughly the same as "Advanced" setting interface in the above, but with a "=" button and a box displaying the operation result. Besides, the variable boxes here require users to input the variable values rather than tag names.
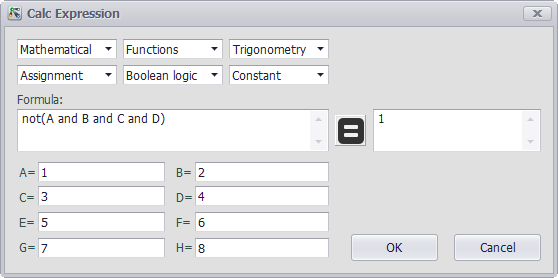
To verify the expression is correct or not, users can click this buttonto get the result, then review it to see its correctness. After the expression has been verified, click "OK" button to update the value; if users do not want to update it, click "Cancel" button.
Function and Operator Description
Through the drop-down boxes, users can set the functions and operators calculation tag supports, which is divided into five categories: "Mathematical", "Functions", "Trigonometry", "Assignment" and "Boolean logic". Moreover, "Constant" box is also provided, allowing users to select from three constants: pi (the ratio of the circumference to the diameter of a circle), epsilon (the smallest positive double value that is greater than zero) and inf (infinity).
As shown in the figure below, the functions or operators listed in the box can be classified into three types: 1. With no brackets, this indicates binary operations (labeled with 1); 2. With brackets but no comma, this means this function only has one parameter (labeled with 2); 3. With brackets and comma, this means the function supports more than one parameter (labeled with 3).
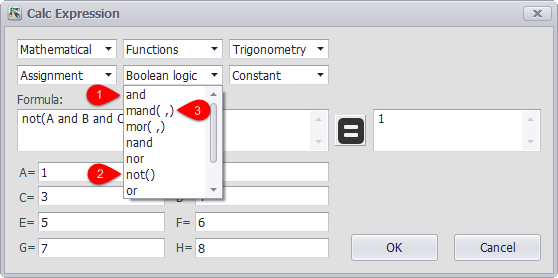
All functions and operators are described as follows:
(0) Arithmetic & Assignment Operators
| OPERATOR | DEFINITION |
|---|---|
| + | Addition between x and y. (eg: x + y) |
| - | Subtraction between x and y. (eg: x - y) |
| * | Multiplication between x and y. (eg: x * y) |
| / | Division between x and y. (eg: x / y) |
| % | Modulus of x with respect to y. (eg: x % y) |
| ^ | x to the power of y. (eg: x ^ y) |
(1) Equalities & Inequalities
| OPERATOR | DEFINITION |
|---|---|
== or = | True only if x is strictly equal to y. (eg: x == y) |
<> or != | True only if x does not equal y. (eg: x <> y or x != y) |
< | True only if x is less than y. (eg: x < y) |
<= | True only if x is less than or equal to y. (eg: x <= y) |
> | True only if x is greater than y. (eg: x > y) |
>= | True only if x is greater than or equal to y. (eg: x >= y) |
(2) Boolean Operations
| OPERATOR | DEFINITION |
|---|---|
| true | True state or any value other than zero (typically 1). |
| false | False state, value of exactly zero. |
| and | Logical AND, True only if x and y are both true. (eg: x and y) |
| mand | Multi-input logical AND, True only if all inputs are true. Left to right short-circuiting of expressions. (eg: mand(x > y, z < w, u or v, w and x)) |
| mor | Multi-input logical OR, True if at least one of the inputs are true. Left to right short-circuiting of expressions. (eg: mor(x > y, z < w, u or v, w and x)) |
| nand | Logical NAND, True only if either x or y is false. (eg: x nand y) |
| nor | Logical NOR, True only if the result of x or y is false. (eg: x nor y) |
| not | Logical NOT, Negate the logical sense of the input. (eg: not(x and y) == x nand y) |
| or | Logical OR, True if either x or y is true. (eg: x or y) |
| xor | Logical XOR, True only if the logical states of x and y differ. (eg: x xor y) |
| xnor | Logical XNOR, True iff the biconditional of x and y is satisfied. (eg: x xnor y) |
& | Similar to AND but with left to right expression short circuiting optimisation. (eg: (x & y) == (y and x)) |
| ` | ` |
(3) General Purpose Functions
| FUNCTION | DEFINITION |
|---|---|
| abs | Absolute value of x. (eg: abs(x)) |
| avg | Average of all the inputs. (eg: avg(x,y,z,w,u,v) == (x + y + z + w + u + v) / 6) |
| ceil | Smallest integer that is greater than or equal to x. |
| clamp | Clamp x in range between r0 and r1, where r0 < r1. (eg: clamp(r0,x,r1)) |
| equal | Equality test between x and y using normalised epsilon |
| erf | Error function of x. (eg: erf(x)) |
| erfc | Complimentary error function of x. (eg: erfc(x)) |
| exp | e to the power of x. (eg: exp(x)) |
| expm1 | e to the power of x minus 1, where x is very small. (eg: expm1(x)) |
| floor | Largest integer that is less than or equal to x. (eg: floor(x)) |
| frac | Fractional portion of x. (eg: frac(x)) |
| hypot | Hypotenuse of x and y (eg: hypot(x,y) = sqrt(xx + yy)) |
| iclamp | Inverse-clamp x outside of the range r0 and r1. Where r0 < r1. If x is within the range it will snap to the closest bound. (eg: iclamp(r0,x,r1)) |
| inrange | In-range returns true when x is within the range r0 and r1. Where r0 < r1. (eg: inrange(r0,x,r1)) |
| log | Natural logarithm of x. (eg: log(x)) |
| log10 | Base 10 logarithm of x. (eg: log10(x)) |
| log1p | Natural logarithm of 1 + x, where x is very small. (eg: log1p(x)) |
| log2 | Base 2 logarithm of x. (eg: log2(x)) |
| logn | Base N logarithm of x, where n is a positive integer. (eg: logn(x,8)) |
| max | Largest value of all the inputs. (eg: max(x,y,z,w,u,v)) |
| min | Smallest value of all the inputs. (eg: min(x,y,z,w,u)) |
| mul | Product of all the inputs. (eg: mul(x,y,z,w,u,v,t) == (x * y * z * w * u * v * t)) |
| ncdf | Normal cumulative distribution function. (eg: ncdf(x)) |
| nequal | Not-equal test between x and y using normalised epsilon |
| pow | x to the power of y. (eg: pow(x,y) == x ^ y) |
| root | Nth-Root of x, where n is a positive integer. (eg: root(x,3) == x^(1/3)) |
| round | Round x to the nearest integer. (eg: round(x)) |
| roundn | Round x to n decimal places where n > 0 and is an integer. (eg: roundn(1.2345678,4) == 1.2346) |
| sgn | Sign of x, -1 where x < 0, +1 where x > 0, else zero. (eg: sgn(x)) |
| sqrt | Square root of x, where x >= 0. (eg: sqrt(x)) |
| sum | Sum of all the inputs. (eg: sum(x,y,z,w,u,v,t) == (x + y + z + w + u + v + t)) |
| trunc | Integer portion of x. (eg: trunc(x)) |
(4) Trigonometry Functions
| FUNCTION | DEFINITION |
|---|---|
| acos | Arc cosine of x expressed in radians. Interval [-1, +1]. (eg: acos(x)) |
| acosh | Inverse hyperbolic cosine of x expressed in radians. (eg: acosh(x)) |
| asin | Arc sine of x expressed in radians. Interval [-1, +1]. (eg: asin(x)) |
| asinh | Inverse hyperbolic sine of x expressed in radians. (eg: asinh(x)) |
| atan | Arc tangent of x expressed in radians. Interval [-1, +1]. (eg: atan(x)) |
| atan2 | Arc tangent of (x / y) expressed in radians. [-pi, +pi]. (eg: atan2(x,y)) |
| atanh | Inverse hyperbolic tangent of x expressed in radians. (eg: atanh(x)) |
| cos | Cosine of x. (eg: cos(x)) |
| cosh | Hyperbolic cosine of x. (eg: cosh(x)) |
| cot | Cotangent of x. (eg: cot(x)) |
| csc | Cosecant of x. (eg: csc(x)) |
| sec | Secant of x. (eg: sec(x)) |
| sin | Sine of x. (eg: sin(x)) |
| sinc | Sine cardinal of x. (eg: sinc(x)) |
| sinh | Hyperbolic sine of x. (eg: sinh(x)) |
| tan | Tangent of x. (eg: tan(x)) |
| tanh | Hyperbolic tangent of x. (eg: tanh(x)) |
| deg2rad | Convert x from degrees to radians. (eg: deg2rad(x)) |
| deg2grad | Convert x from degrees to gradians. (eg: deg2grad(x)) |
| rad2deg | Convert x from radians to degrees. (eg: rad2deg(x)) |
| grad2deg | Convert x from gradians to degrees. (eg: grad2deg(x)) |