EdgeHub Private Network (EPN)
Changelog
| Version | Author | Update Date | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.4.0 | ITsung.Shen | 2025/04/21 | First Version |
1. Introduction
EdgeHub Private Network (EPN) provides a simplified process for establishing cross-subnet remote connections. It allows users to securely access gateway devices from a PC and update terminal programs. This applies to terminal devices with serial or Ethernet interfaces.
Because remote access channels involve both network and device configurations, setup can be complex. EPN simplifies this process, making access to terminal devices (such as PLCs) more intuitive and automated, thereby lowering the technical barrier.
The EdgeHub Private Network consists of the following core components:
- EPN Server
- Responsible for establishing secure remote access channels between EPN Devices and EpnClients.
- EPN Device
- A device that supports the EPN feature, capable of creating a remote access channel and allowing tunneling to its connected sub-devices.
- Currently, only
EdgeLinkdevices are supported (firmware version 2.8.4.2 or above). When a device of typeEdgeLinkis added via DPM, it will automatically be included as an EPN Device.
- EpnClient
- Installed on the user’s PC, used to establish a remote access channel to reach terminal devices.
- Terminal
- Refers to sub-devices under an EPN Device, connected via subnet or serial interfaces (e.g., sensors, PLCs).
EdgeHub users can manage the above components using the following tools:
- Direct Access Portal
- A web interface on the EdgeHub platform used to manage EPN-related settings, including servers, devices, clients, and terminals.
- For more details, please refer to the Direct Access documentation.
- EdgeHub Utility
- A desktop tool for EdgeHub users to access EPN-related features from a PC.
- Currently supports EpnClient connections, EPN Device wake-up and connection, and Terminal management.
- For more details, please refer to the EdgeHub Utility documentation.
The workflow of the EdgeHub Private Network is illustrated below:
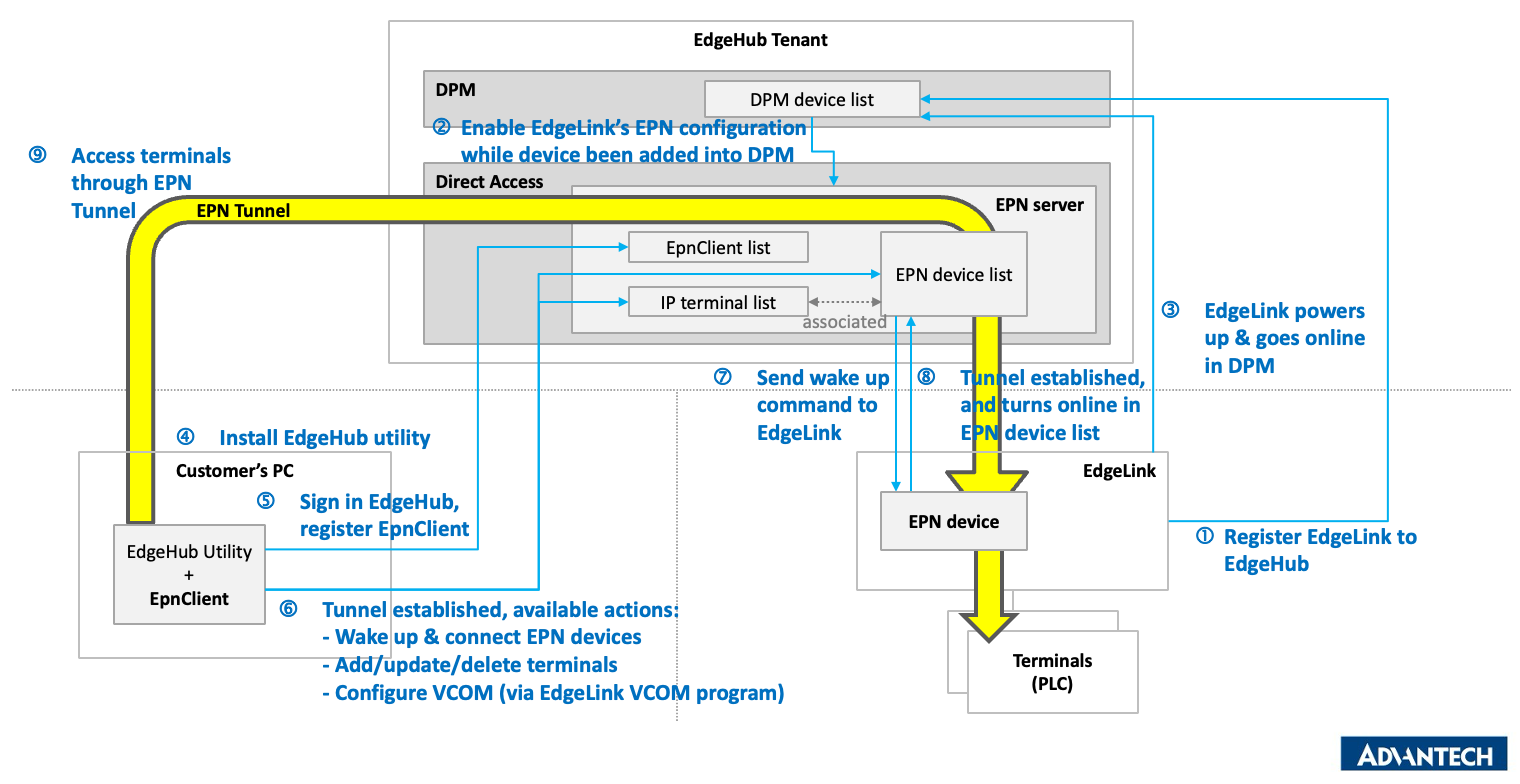
- Add an EdgeLink device via the EdgeHub Device Management feature.
- EdgeHub detects that the device is of type
EdgeLinkand supports EPN, so it automatically enables EPN settings and adds the device to the EPN device list. - After the EdgeLink device powers on, its online status can be seen in the Device Management view (but it is not yet online in the EPN device list).
- Install the EdgeHub Utility.
- Log into EdgeHub using the EdgeHub Utility and register the EpnClient.
- Once registration is complete, the EpnClient establishes a secure tunnel with the EPN Server, and the following operations become available via the EdgeHub Utility:
- Add / Edit / Delete terminals
- Wake up & connect to EPN Devices
- Perform VCOM configuration on EPN Devices (via EdgeLink VCOM software)
- The EPN Server sends a wake-up command to the EPN Device (EdgeLink).
- The EPN Device establishes a channel with the EPN Server and appears as online in the EPN device list.
- The EpnClient can now access the EPN Device and its terminals through the EPN tunnel, allowing users to configure and control terminal devices.
2. EPN Network Architecture & Message Flow
This section explains the architecture of the EPN network and provides an example of how a message is transmitted from a PC to a terminal via the EPN Server.
Please refer to the diagram below:
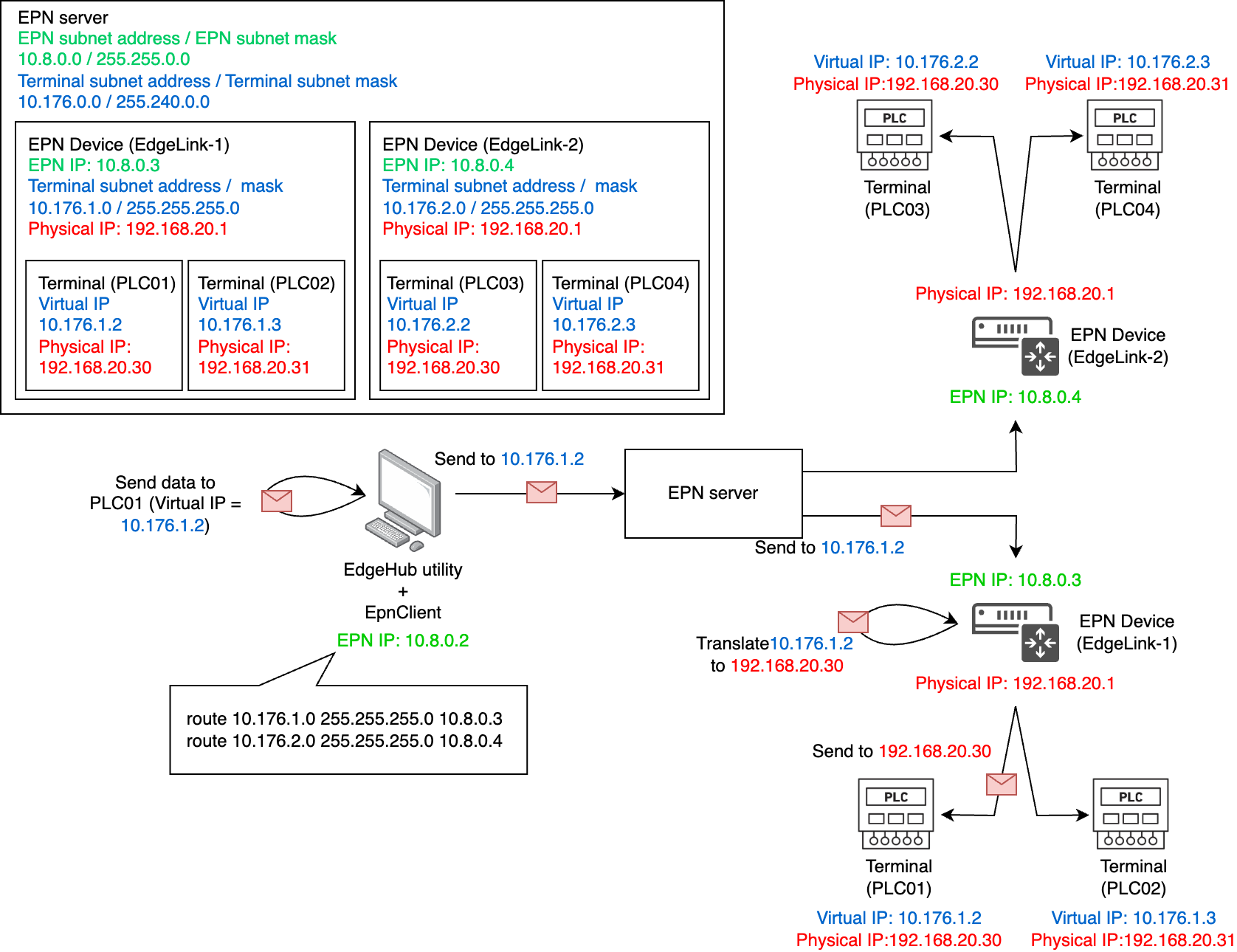
2.1 Component Relationships
EPN Server
In an EPN environment, the EPN Server establishes subnet connections between the EpnClient and EPN Devices/Terminals.
Based on the network layout illustrated above:
-
EPN Subnet address / EPN Subnet mask
- Used to assign EPN subnet IP addresses to EPN Devices and EpnClients.
In the diagram above:- EPN Subnet address = 10.8.0.0
- EPN Subnet mask = 255.255.0.0
- This means the EPN Server can allocate IPs in the range of 10.8.0.1 ~ 10.8.255.254 — a total of 65,534 available addresses — to EPN Devices and EpnClients.
- Used to assign EPN subnet IP addresses to EPN Devices and EpnClients.
-
Terminal subnet address / Terminal subnet mask
-
Used to assign virtual subnet segments for Terminal devices.
In the diagram:- Terminal subnet address = 10.176.0.0
- Terminal subnet mask = 255.240.0.0
- Therefore, the available virtual IP range for the EPN Server is:
10.176.0.1 ~ 10.191.255.254 — a total of 1,048,574 usable IP addresses. - Since each Terminal belongs to its respective EPN Device, the EPN Server will assign a dedicated /24 subnet to each EPN Device.
Each /24 subnet contains 256 IP addresses, of which 254 are usable for connecting underlying terminals (e.g., PLCs).
-
Based on this calculation, a single EPN Server can support up to 4,096 EPN Devices.
EPN Device
-
EPN IP
- Each EPN Device receives an EPN network IP address from the EPN Server to accept various operational commands from the EpnClient.
- In the diagram above, the EPN IP assigned to EdgeLink-1 is 10.8.0.3.
-
Terminal subnet address / Terminal subnet mask
- As mentioned earlier, each EPN Device is assigned a dedicated subnet (/24) to serve its connected terminals.
In the diagram above:- Terminal subnet address = 10.176.1.0
- Terminal subnet mask = 255.255.255.0
- This means the virtual IP range for this EPN Device is:
10.176.1.1 ~ 10.176.1.254 — a total of 254 usable IP addresses. - Each virtual IP assigned to a terminal maps to its corresponding physical IP, allowing the EPN Device to forward packets to the terminal.
- As mentioned earlier, each EPN Device is assigned a dedicated subnet (/24) to serve its connected terminals.
-
Physical IP
- The EPN Device and its terminals form a physical subnet connected via LAN cables, and the EPN Device is assigned a physical IP address.
- This IP is used solely for local communication with terminal devices (e.g., PLCs) and cannot be accessed directly from external networks.
- In the diagram, the physical IP of EdgeLink-1 is 192.168.20.1.
Terminal
Terminal devices (e.g., PLCs, IO module...etc.) connected under an EPN Device.
-
Virtual IP
- A virtual IP address assigned by the EPN Server to the terminal, used to map to the terminal’s physical IP.
- In the diagram above, the Virtual IP of PLC01 is 10.176.1.2.
-
Physical IP
- The physical IP address of the terminal, used for local communication with the EPN Device.
- In the diagram, the Physical IP of PLC01 is 192.168.20.30.
EpnClient
EpnClient is installed on the user's PC and is used to connect to the EPN network and control EPN Devices and Terminals.
- EPN IP
- Each EpnClient receives an EPN network IP address from the EPN Server to issue operational commands to EPN Devices and Terminals.
- In the diagram above, the EPN IP assigned to the EpnClient is 10.8.0.2.
2.2 Message Flow
Scenario
-
A PC with an EpnClient installed also has control software for PLC01.
The goal is to establish a tunnel via the EPN network to remotely control PLC01.
Message Flow
- The EpnClient first retrieves the virtual IP of PLC01 (Virtual IP = 10.176.1.2), which can be found via the Direct Access portal or the EdgeHub Utility.
- The EpnClient sends PLC control commands to 10.176.1.2. Based on routing rules, it determines that this address belongs to the EPN virtual network range.
- The packet is routed into the EPN tunnel and reaches the EPN Server.
- The EPN Server uses the virtual subnet mapping table to forward the packet to EdgeLink-1 (which manages the 10.176.1.0/24 subnet).
- EdgeLink-1 receives the packet and translates the virtual IP 10.176.1.2 to its corresponding physical IP 192.168.20.30.
- EdgeLink-1 forwards the packet to the physical terminal PLC01 (IP: 192.168.20.30).
- PLC01 successfully receives the packet, completing the communication.
Through this message flow, the EpnClient is able to remotely control PLC01.
3. System Limitation
The following outlines several system limitations of the EPN network.
3.1 Remote Maintenance of Terminals
To remotely control terminal devices via the EPN network, the following conditions must be met:
- The Interface Type of the EPN Server must be set to
TAPmode. - The EPN Device must support Virtual IP to Physical IP forwarding rules (currently supported by
EdgeLinkdevices with firmware version 2.8.4.2 or above).
3.2 Maximum Number of EPN Remote Access tunnels
EdgeHub imposes the following limitations on the number of concurrent EPN remote access tunnels:
- A maximum of
10EPN remote access tunnels can be active simultaneously under a single tenant. - This limit applies to the combined total of both EpnClients and EPN Devices.
4 Open Source Components Used
This system internally uses the following open-source software components:
-
OpenVPN – https://openvpn.net/
License: GNU General Public License v2 (GPLv2)
OpenVPN is used as the core VPN engine for establishing encrypted communication tunnels within our platform. -
docker-openvpn by Kyle Manna – https://github.com/kylemanna/docker-openvpn
License: MIT
This component is used to facilitate the container-based deployment and management of OpenVPN. No modifications have been made.
These components are used internally as part of our managed infrastructure and are not distributed to end users. For license details, please refer to the links above.